In recent years, there has been an alarming increase in cancer cases among people under the age of 49, especially among women. A British study published in the scientific journal BMJ Oncology revealed that cancer cases in this age group increased by approximately 80% between 1990 and 2019, leading to a total of 3.26 million new diagnoses in 2019, compared to 1.8 million cases recorded in 1990.
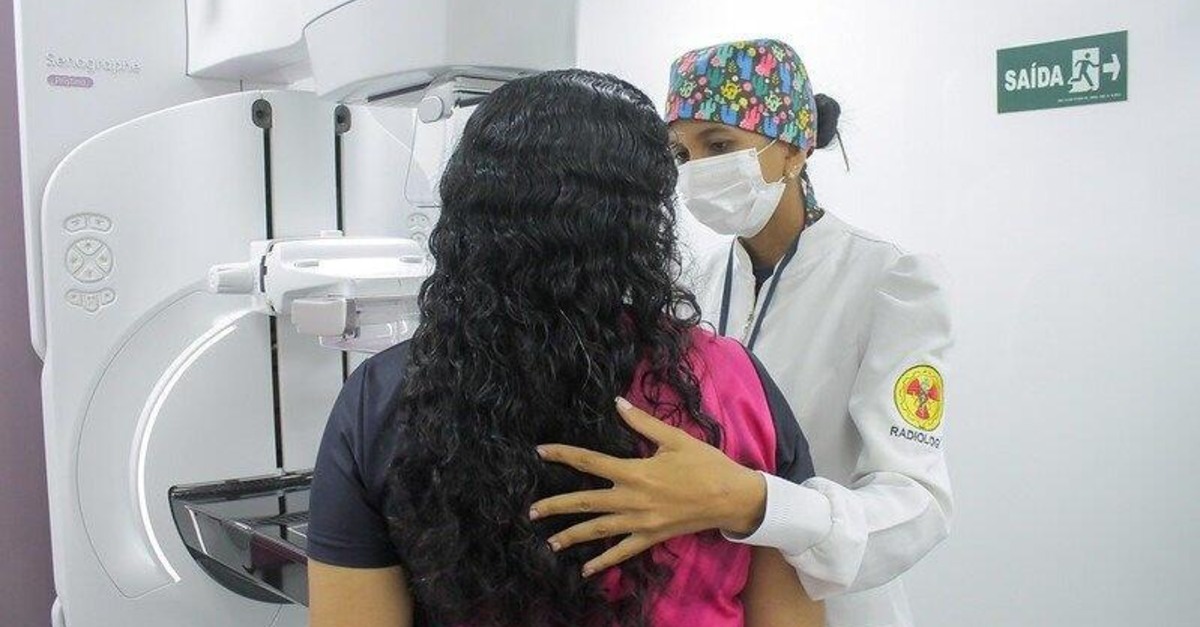
breast cancer
Breast cancer stands out as the most frequently diagnosed type and, unfortunately, it is also among the deadliest. In addition, cancers of the trachea, lungs, intestines and stomach were among the main causes of this alarming trend. Analysis of the data indicates a relationship between the increase in cases and known risk factors, such as poor diet, smoking and alcohol consumption.
Continues after ad
Continues after ad
Risk factors
Poor nutrition abuse, characterized by diets high in saturated fat and lacking in essential nutrients, is emerging as a major risk factor. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, long linked to the development of various types of cancer, are also emerging as suspects in this worrying scenario.
Despite evidence pointing to these risk factors, the exact reason for the significant increase in cancer rates in young people remains unclear. The intersection of diverse genetic, environmental and behavioral elements makes it difficult to pinpoint a single culprit. An in-depth understanding of the reasons behind this growth becomes crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Hormonal factors and speed
Among the study results, two hormonal factors linked to breast cancer stand out: age at first menstrual period (menarche) and breastfeeding. The speed of these events appears to influence the early appearance of breast tumors, adding additional complexity to the equation.

“Writer. Analyst. Avid travel maven. Devoted twitter guru. Unapologetic pop culture expert. General zombie enthusiast.”