Our planet, teeming with life, is unique among all that we have been able to explore in the universe thus far. From our axial tilt, which prevents many temperature extremes, to our location in the habitable zone of our star, life on Earth depends on many cycles that, finely balanced and intertwined, allowed their union to produce the exact conditions we need. to thrive. According to scientists, there was an alarming change in one of these cycles.
The exact cycle affected relates to the Earth’s energy system, and the input and output of energy received from the Sun.
The weather is changing... my knees don't lie!
In recent decades, we have witnessed changes in the planet's temperature and other climatic indicators. There is talk of pollution, but there is a lot behind these changes that affect life here in this corner of the universe.
At stake will be the energy cycle that dictates all planetary climate systems. On Mars, the seasonal change in energy imbalance is thought to be about 15.3% between seasons on the Red Planet, compared to 0.4% on Earth. This change on Mars causes the infamous Martian dust storms.
secondly What the scholars saidFor some time, prior to the 1850s, the fluctuating energy cycle on Earth was relatively balanced. However, we have now created an imbalance that has recently doubled in just 15 years.
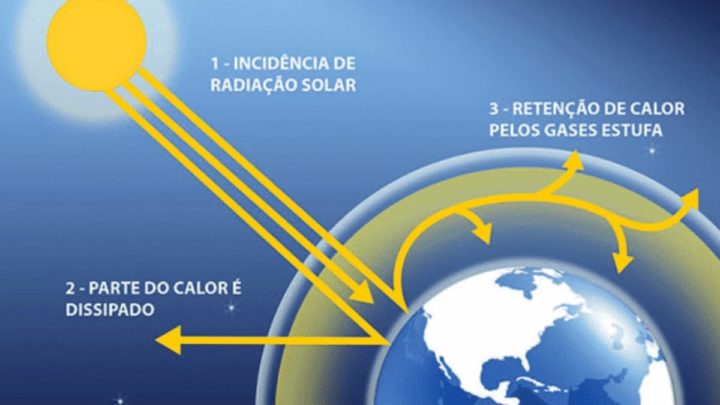
The net energy imbalance is calculated by analyzing how much heat is absorbed by the sun and how much is able to radiate back into space.
It is not yet possible to measure the defect directly, the only practical way to estimate it is through an inventory of changes in power.
explain the Atmospheric scientist Kevin Trenberth National Center for Atmospheric Research.
Albedo or the reflection coefficient is changing and that's...not good!
Trenberth and atmospheric physicist Lijing Cheng of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reviewed data from all components of the climate system: land, ice, oceans and atmosphere between 2000 and 2019, to make an inventory of these changes.
Earth's atmosphere reflects nearly a quarter of the energy that hits it, unlike the moon, which absorbs the full impact of the sun's energy, resulting in surface temperatures of around 100°C. The moon then absorbs most of this energy and is radiated back into space as infrared thermal radiation, more commonly known as heat.
Yes, of course what makes all the difference between the Earth and the Moon is our atmosphere. Some molecules in our atmosphere capture this heat before it reaches space and continue to cling to it. Unfortunately for us, these are greenhouse gases, which are now Effectively wrapping the planet in a very dirty blanket in the upper part of the atmosphere.
As the scientists explain in their work, this trapped excess energy not only changes where it ends up, but also affects your environment on the way to your destination.
Global warming has different effects
The rise in temperature on our planet has been the subject of many debates and attempts at interpretation. However, this increase is just a product of this extra energy. Only 4% of this energy goes to increasing the Earth's temperature and another 3% goes to melting ice.
Almost 93% is absorbed by the ocean and we are already seeing unpleasant consequences. Although less than 1% of excess energy revolves around our atmosphere, it is enough to increase the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events, from droughts to floods.
However, increased atmospheric turbulence can also be beneficial.
These weather events move energy and help the climate system get rid of energy by radiating it into space.
Explain to the investigators.
Clouds and ice also help reflect solar radiation before it becomes long wave heat captured by the gases. But both reflective clouds and ice are reduced due to disturbances in this energy cycle.
In this data, there is still a lot of information missing for a comprehensive model of the Earth system that accurately predicts specific outcomes beyond the short term. But time changes and in what way!

“Friendly zombie fanatic. Analyst. Coffee buff. Professional music specialist. Communicator.”